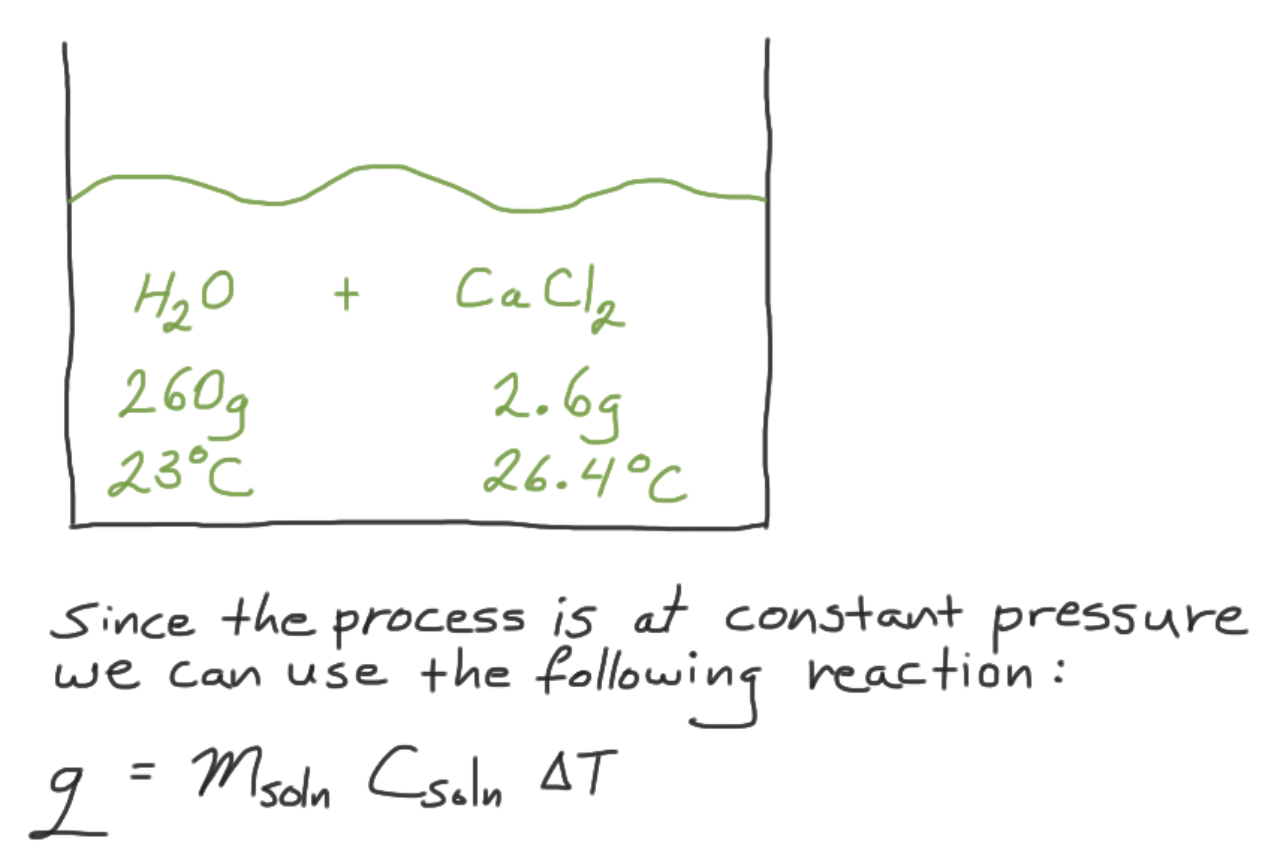
2.6 g of CaCl 2 (s) was dissolved in 260 g of water at 23 ˚ C and constant pressure. If the final temperature is 26.4 ˚ C, what is the ent...
2.6 g of CaCl2 (s) was dissolved in 260 g of water at 23 ˚C and constant pressure. If the final temperature is 26.4 ˚C, what is the enthalpy change of dissolving the solid?
Consider the specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J/g ˚C.
The initial temperature is 23 ˚C, which is the temperature of the water. Once you add the solid, it starts dissolving resulting in a final temperature of 26.4 ˚C.
The fact that the temperature of dissolving the solid is higher than the initial temperature of the water indicates that the process is releasing energy, and the water is absorbing that energy.
Therefore, the process is exothermic.
![[headerImage]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/a/AVvXsEjUOYgMVdlvKlz8nrbbh9IHsIFxccdyYSVPijXKJ6MmdtCQKCiXv9TxOVmVrk1gBD4uRvT4S3-r3vX85WK5KD3GhhE18pQCoD0h2OKGY9tbmOZn3wfQTP9V3m2XtdnxcIdi6-Cc-osPk_kApHlkRIdFKoHbW8N_Mcef2WeJFtolOi8pAJba1x8Rnchy=s16000)